Roman Catholic
St Sigismund parish
05-507 Słomczyn
85 Wiślana Str.
Konstancin deanery
Warsaw archdiocese, Poland
full list:
displayClick to display full list

searchClick to search full list by categories
wyświetlKliknij by wyświetlić pełną listę po polsku

szukajKliknij by przeszukać listę wg kategorii po polsku
Martyrology of the clergy — Poland
XX century (1914 – 1989)
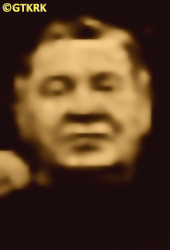
personal data
surname
SOPUCH
forename(s)
Stanislav (pl. Stanisław)
function
religious cleric
creed
Latin (Roman Catholic) Church RCmore on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2014.09.21]
congregation
Society of Jesus SImore on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2014.09.21]
(i.e. Jesuits)
diocese / province
Greater Poland‐Mazovian province SI
Polish Province SI (1918‐1926)
Galicia Province SI (till 1918)
date and place
of death
26.02.1941

Warsawtoday: Warsaw city pov., Masovia voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.10.09]
details of death
In 1914, as a result of the Russian offensive at the beginning of World War I, Lviv and most of Eastern Galicia, i.e. part of the Germ. Königreich Galizien und Lodomerien (Engl.
Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria) Crown Land and province, belonging to the Austro–Hungarian Monarchy, came under Russian occupation. When the Russians were defeated in the Battle of Gorlice in 05.1915, they began to withdraw to the east. On 19.06.1915 arrested by the Russians in Lviv. Held in a court prison for a day, then on 20.06.1915, among 37 hostages — 12 Poles, 10 Ruthenians and 15 Jews — taken out of the city. Initially in a freight car, from Zdolbuniv in a passenger car, on 23.06.1915 — the day after Lviv was retaken by Austro–Hungarian troops — taken to Kiev. There, after separating the Jewish hostages, held in a villa, converted into a jail, called in Rus. „Польский арестный домъ” (Eng. „Polish house arrest”).
Released on 07.08.1915, but without the possibility of return. Travelled, among other places, „to Siberia”, to minister to other Polish refugees and hostages.
To his diocese returned after the separatist Treaty of Brest–Litovsk of 03.03.1918, signed by Germany and Austria–Hungary with Bolshevik Russia, de facto ending the military operations of World War I on the Eastern Front and establishing a Ukrainian state with its capital in Kiev, controlled by Germany.
After German invasion of Poland on 01.09.1939 (Russians invaded Poland 17 days later) and start of the World War II arrested by the Germans on 05.09.1939.
Jailed in Kalisz.
Released after a fortnight.
Settled in a Franciscan convent in Kalisz.
In 10.1939 arrested by the Germans again.
Jailed in Łódź transit camp.
On 13.10.1940 released and deported to Jędrzejów in Germ. Generalgouvernement (Eng. General Governorate), without the right to go back to Kalisz.
Settled in Warszaw, where soon perished without recovering.
cause of death
extermination
perpetrators
Germans
sites and events
GeneralgouvernementClick to display the description, Łódź (Sterling Str.)Click to display the description, KaliszClick to display the description, «Intelligenzaktion»Click to display the description, Ribbentrop‐MolotovClick to display the description, Pius XI's encyclicalsClick to display the description
date and place
of birth
22.04.1869

Kożuchówtoday: Wiśniowa gm., Strzyżów pov., Subcarpathia voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.12.18]
presbyter (holy orders)
ordination
04.07.1897
Krakówtoday: Kraków city pov., Lesser Poland voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.06.07]
positions held
1938 – 1939
superior — Kalisztoday: Kalisz city pov., Greater Poland voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2020.12.16] ⋄ Visitation of the Blessed Virgin Mary monastery, Jesuits SI
1935 – 1938
Provincial — Greater Poland–Mazovian Province, Jesuits SI — initiator of the construction of the „Writers' House” monastery, 61 Rakowiecka Str.
1927 – 1931
superior — Łódźtoday: Łódź city pov., Łódź voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.07.18] ⋄ Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary monastery, Jesuits SI
1928 – 1930
parish priest — ŁódźBałuty district
today: Łódź city pov., Łódź voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.07.18] ⋄ Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary RC parish ⋄ Łódźtoday: Łódź city pov., Łódź voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.07.18] RC deanery
1919 – 1926
Provincial — Polish Province, Jesuits SI — i.a. initiator of the construction of the kolegium „Bobolanum” college in Lublin; also: retreatist and people's missionary
1913 – 1915
superior — Lvivtoday: Lviv urban hrom., Lviv rai., Lviv obl., Ukraine
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2022.01.16] ⋄ St Peter and St Paul the Apostles monastery, Jesuits SI
1908 – 1913
superior — Lvivtoday: Lviv urban hrom., Lviv rai., Lviv obl., Ukraine
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2022.01.16] ⋄ St Joseph monastery (Retreat House), Jesuits SI
1904 – 1908
superior — Lvivtoday: Lviv urban hrom., Lviv rai., Lviv obl., Ukraine
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2022.01.16] ⋄ St Peter and St Paul the Apostles monastery, Jesuits SI
1899 – 1904
friar — Lvivtoday: Lviv urban hrom., Lviv rai., Lviv obl., Ukraine
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2022.01.16] ⋄ St Peter and St Paul the Apostles monastery, Jesuits SI — operarius, preacher, organizer of Catholic workers' associations
1897 – 1899
friar — Krakówtoday: Kraków city pov., Lesser Poland voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.06.07] ⋄ St Barbara monastery, Jesuits SI — operarius, preacher, organizer of Catholic workers' associations
1894 – 1897
student — Krakówtoday: Kraków city pov., Lesser Poland voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.06.07] ⋄ college (Lat. Collegium Maximum SS. Cordis Iesu), 26 Kopernik Str., monastery (by the Holiest Heart of Jesus church), Jesuits SI
1891 – 1894
educator — Bunkovychin .Khyriv
today: Khyriv urban hrom., Sambir rai., Lviv obl., Ukraine
more on
uk.wikipedia.org
[access: 2022.11.09] ⋄ St Joseph College („Khyriv” Scientific and Educational Institute), Jesuits SI
1888 – 1891
student — Ternopiltoday: Ternopil urban hrom., Ternopil rai., Ternopil obl., Ukraine
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2020.11.20] ⋄ Immaculate Conception of the Blessed Virgin Mary monastery, Jesuits SI
1884 – 1885
novitiate — Stara Wieśtoday: Brzozów gm., Brzozów pov., Subcarpathia voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.12.18] ⋄ Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary monastery, Jesuits SI
24.07.1884
accession — Stara Wieśtoday: Brzozów gm., Brzozów pov., Subcarpathia voiv., Poland
more on
en.wikipedia.org
[access: 2021.12.18] ⋄ Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary monastery, Jesuits SI
others related
in death
CHAMCZUKClick to display biography Gregory, CZUBATYClick to display biography Theodore, KWIATKOWSKIClick to display biography Stanislav Ignatius, KWITClick to display biography Basil Steven, SZCZEPANIUKClick to display biography Nicholas
sites and events
descriptions
Generalgouvernement: After the Polish defeat in the 09.1939 campaign, which was the result of the Ribbentrop‐Molotov Pact and constituted the first stage of World War II, and the beginning of German occupation in part of Poland (in the other, eastern part of Poland, the Russian occupation began), the Germans divided the occupied Polish territory into five main regions. In two of them new German provinces were created, two other were incorporated into other provinces. However, the fifth part was treated separately, and in a political sense it was supposed to recreate the German idea from 1915 (during World War I, after the defeat of the Russians in the Battle of Gorlice in 05.1915) of creating a Polish enclave within Germany. Illegal in the sense of international law, i.e. Hague Convention, and public law, managed by the Germans according to separate laws — especially established for the Polish Germ. Untermenschen (Eng. subhumans) — till the Russian offensive in 1945 it constituted part of the Germ. Großdeutschland (Eng. Greater Germany). Till 31.07.1940 formally called Germ. Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete (Eng. General Government for the occupied Polish lands) — later simply Germ. Generalgouvernement (Eng. General Governorate), as in the years 1915‐1918. From 07.1941, i.e. after the German attack on 22.06.1941 against the erstwhile ally, the Russians, it also included the Galicia district, i.e. the Polish pre‐war south‐eastern voivodeships. A special criminal law was enacted and applied to Poles and Jews, allowing for the arbitrary administration of the death penalty regardless of the age of the „perpetrator”, and sanctioning the use of collective responsibility. After the end of the military conflict of the World War UU, the government of the Germ. Generalgouvernement was recognized as a criminal organization, and its leader, governor Hans Frank, guilty of war crimes and crimes against humanity and executed. (more on: en.wikipedia.orgClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2024.12.13])
Łódź (Sterling Str.): Prison for men, founded in 1893, in a tenement houses at 16/18 Sterling Str. in Łódź, by the Russian occupiers (during partitions of Poland). In the interwar period, a Polish state prison. During World War II, a German police prison, used also by the Germ. Geheime Staatspolizei (Eng. Secret State Police), i.e. Gestapo. The prisoners were held in two three‐story buildings with 53 cells and 5 „sick rooms”. Interrogations of arrested Poles, combined with torture, as well as executions ‐ by hanging — were held there. After the German defeat and the beginning of the Russian occupation, the prison of the Commie‐Nazi of State Security Office UB — the unit of Russian genocidal MGB. Executions continued to take place there, this time of Germans and Poles convicted of collaborating with the German occupier, as well as of those convicted of anti‐communist activities and ordinary criminals. Closed in 1964. (more on: pl.wikipedia.orgClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2015.09.30])
Kalisz: Prison for men and women built in 1840‐1846, during the Russian occupation. It consisted of c. 120 individual cells. After the outbreak of World War II and start of German occupation, it was a pre‐trial detention center and a prison — initially Germ. Gefängnis (Eng. prison), from 10.03.1941 Germ. Haftanstalt (Eng. jail), from 01.1942 Germ. Stammlager/Haftanstalt (Eng. main penal camp / jail) — administered by the German Germ. Geheime Staatspolizei (Eng. Secret State Police), i.e. Gestapo. Mainly Poles, but also Germans, including those considered to be political prisoners (members of the Polish resistance movement), were held there. Inmates — if they were not murdered as a result of torture or sentenced to death — were next transported to concentration camps. The prison was overcrowded — e.g. on 30.04.1943, 422 men and 126 women were held there. The prisoners were tortured. From 18.09.1942, death sentences were carried out on Poles — c. 700 people were murdered in total (shot, hanged, and those who died as a result of torture and diseases). In total, over 15,000 people passed through the prison between 1939 and 1945. After the German defeat and the start of the Russian occupation, the prison was run by the Commie‐Nazi UB, a unit of the genocidal Russian MGB. In 12.1952, 599 people were detained there — some of them soldiers of the clandestine Greater Poland Independent Volunteer Group WARTA and the NSZ, as well as pre—war Polish policemen, and young high school students opposing the Russian occupation. (more on: sw.gov.plClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2022.08.17], www.szukajwarchiwach.gov.plClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2024.12.13])
«Intelligenzaktion»: German: «Intelligenzaktion» (English: „Intelligence Action”) — a German program of extermination of the Polish elite, mainly the intelligentsia and leadership layers, carried out from the beginning of the occupation in w 09.1939 to 04.1940, mainly in territories directly annexed to Germany, but also in the so‐called Germ. Generalgouvernement (Eng. General Governorate), where it was called «AB‐aktion». In the first phase, immediately after the beginning of the German occupation, during military operations carried out by the Germ. Wehrmacht (Eng. Armed Forces) and the genocidal units of the Germ. Einsatzgruppen (Eng. Operational Groups) of the Germ. Sicherheitspolizei (Eng. Security Police), i.e. SiPo, and Germ. Sicherheitsdienst des Reichsführers SS (Eng. Security Service of the Reichsführer SS), i.e. SD, organized by the Germ. Reichssicherheitshauptamt (Eng. Reich Main Security Office), i.e. RSHA, which followed the troops, carried out under the Germ. Unternehmen „Tannenberg” (Eng. Operation „Tannenberg”) — based on the so‐called Germ. Sonderfahndungsliste (Eng. Special Wanted Lists), i.e. proscription lists of Poles considered particularly dangerous to the Third Reich, prepared by the Zentralstelle II/P (Polen) unit of the German RSHA. Later, implemented by the German civilian occupation authorities and the genocidal unit of the Germ. Volksdeutscher Selbstschutz (Eng. Ethnic Germans Self‐Defense), whose members were Germ. Volksdeutsche (Eng. Ethnic Germans), i.e. representatives of the German minority in Poland. According to various sources, these lists, at the beginning of 09.1939, could have contained the details of 61,000—88,000 „dangerous” Poles — although these figures cannot be confirmed. In total, during this genocide, c. 50,000 teachers, Catholic priests, representatives of the landed gentry, freelancers, social and political activists, and retired military personnel were systematically and methodically murdered. Another 50,000 were sent to concentration camps, where only a negligible percentage survived. (more on: en.wikipedia.orgClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2014.10.04])
Ribbentrop‐Molotov: Genocidal Russian‐German alliance pact between Russian leader Joseph Stalin and German leader Adolf Hitler signed on 23.08.1939 in Moscow by respective foreign ministers, Mr. Vyacheslav Molotov for Russia and Joachim von Ribbentrop for Germany. The pact sanctioned and was the direct cause of joint Russian and German invasion of Poland and the outbreak of the World War II in 09.1939. In a political sense, the pact was an attempt to restore the status quo ante before 1914, with one exception, namely the „commercial” exchange of the so‐called „Kingdom of Poland”, which in 1914 was part of the Russian Empire, fore Eastern Galicia (today's western Ukraine), in 1914 belonging to the Austro‐Hungarian Empire. Galicia, including Lviv, was to be taken over by the Russians, the „Kingdom of Poland” — under the name of the General Governorate — Germany. The resultant „war was one of the greatest calamities and dramas of humanity in history, for two atheistic and anti‐Christian ideologies — national and international socialism — rejected God and His fifth Decalogue commandment: Thou shall not kill!” (Abp Stanislav Gądecki, 01.09.2019). The decisions taken — backed up by the betrayal of the formal allies of Poland, France and Germany, which on 12.09.1939, at a joint conference in Abbeville, decided not to provide aid to attacked Poland and not to take military action against Germany (a clear breach of treaty obligations with Poland) — were on 28.09.1939 slightly altered and made more precise when a treaty on „German‐Russian boundaries and friendship” was agreed by the same murderous signatories. One of its findings was establishment of spheres of influence in Central and Eastern Europe and in consequence IV partition of Poland. In one of its secret annexes agreed, that: „the Signatories will not tolerate on its respective territories any Polish propaganda that affects the territory of the other Side. On their respective territories they will suppress all such propaganda and inform each other of the measures taken to accomplish it”. The agreements resulted in a series of meeting between two genocidal organization representing both sides — German Gestapo and Russian NKVD when coordination of efforts to exterminate Polish intelligentsia and Polish leading classes (in Germany called «Intelligenzaktion», in Russia took the form of Katyń massacres) where discussed. Resulted in deaths of hundreds of thousands of Polish intelligentsia, including thousands of priests presented here, and tens of millions of ordinary people,. The results of this Russian‐German pact lasted till 1989 and are still in evidence even today. (more on: en.wikipedia.orgClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2015.09.30])
Pius XI's encyclicals: Facing the creation of two totalitarian systems in Europe, which seemed to compete with each other, though there were more similarities than contradictions between them, Pope Pius XI issued in 03.1937 (within 5 days) two encyclicals. In the „Mit brennender Sorge” (Eng. „With Burning Concern”) published on 14.03.1938, condemned the national socialism prevailing in Germany. The Pope wrote: „Whoever, following the old Germanic‐pre‐Christian beliefs, puts various impersonal fate in the place of a personal God, denies the wisdom of God and Providence […], whoever exalts earthly values: race or nation, or state, or state system, representatives of state power or other fundamental values of human society, […] and makes them the highest standard of all values, including religious ones, and idolizes them, this one […] is far from true faith in God and from a worldview corresponding to such faith”. On 19.03.1937, published „Divini Redemptoris” (Eng. „Divine Redeemer”), in which criticized Russian communism, dialectical materialism and the class struggle theory. The Pope wrote: „Communism deprives man of freedom, and therefore the spiritual basis of all life norms. It deprives the human person of all his dignity and any moral support with which he could resist the onslaught of blind passions […] This is the new gospel that Bolshevik and godless communism preaches as a message of salvation and redemption of humanity”… Pius XI demanded that the established human law be subjected to the natural law of God , recommended the implementation of the ideal of a Christian state and society, and called on Catholics to resist. Two years later, National Socialist Germany and Communist Russia came together and started World War II. (more on: www.vatican.vaClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2023.05.28], www.vatican.vaClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2023.05.28])
sources
personal:
college.holycross.eduClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2012.11.23], pl.wikipedia.orgClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2013.02.15], ipsb.nina.gov.plClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2015.03.01], archive.todayClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2021.12.19]
bibliographical:
„Jesuits on Polish and Lithuanian territory knowledge encyclopedia, 1564‐1995”, Fr Louis Grzebień SI (editor), WAM Printing House, Cracow 1996
original images:
pl.wikipedia.orgClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2015.03.01], ipsb.nina.gov.plClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2015.03.01], www.pbc.biaman.plClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2019.10.13], polona.plClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2025.02.11], sbc.org.plClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2025.02.11], college.holycross.eduClick to attempt to display webpage
[access: 2013.05.19]
LETTER to CUSTODIAN/ADMINISTRATOR
If you have an Email client on your communicator/computer — such as Mozilla Thunderbird, Windows Mail or Microsoft Outlook, described at WikipediaPatrz:
en.wikipedia.org, among others — try the link below, please:
LETTER to CUSTODIAN/ADMINISTRATORClick and try to call your own Email client
If however you do not run such a client or the above link is not active please send an email to the Custodian/Administrator using your account — in your customary email/correspondence engine — at the following address:
giving the following as the subject:
MARTYROLOGY: SOPUCH Stanislav
To return to the biography press below:
 Click to return to biography
Click to return to biography